Mechanics
Definitions
Mass
Basic property of matter. Numerous definitions (Wikipedia), but simplest in terms of inertia (F=ma), mass-energy equivalence (e=mc2) or atomic mass using Avagadro’s number.
It may also be determined using gravitational effects. If the strength of the gravitational field is known (g), then a given mass (m) will experience a predictable force i.e it will have a predictable weight (w).
In equation 1, g is measured in Newtons, m in kilograms and g in ms−2.
Force
From Newton’s second law, a force is ’That which changes or tends to change the state of an object from rest or uniform motion in a straight line’. In equation 2, force (F) is measured in Newtons, mass (m) in kilograms and acceleration (a) in ms−2.
Energy
An abstract quantity, measure in Joules and which represents the ability of a system to do work. Energy can be neither destroyed, nor created (law of conservation of energy) but its form can be transformed (mechanical, thermal, kinetic etc.).
Work
Describes the expenditure of energy (measured in Joules).
When considering a moving object (e.g. pushing a box along the floor), the energy expended is proportional to the force applied (Newtons) and the distance moved (meters) i.e.
When thinking about gases (e.g. Fig. 1), this can be modified using equation 4 (where F is force (N), P is pressure (N m−2) and a is area (m−2) ), to give equation 5. To make things simpler, when the piston of area ’a’ m−2 moves a distance d meters, this represents a change in volume ΔV m−3 and the equation becomes as in 6 (N.B. This is true for isobaric changes only. See Physics hypertextbook and PV diagrams for more detailed descriptions.
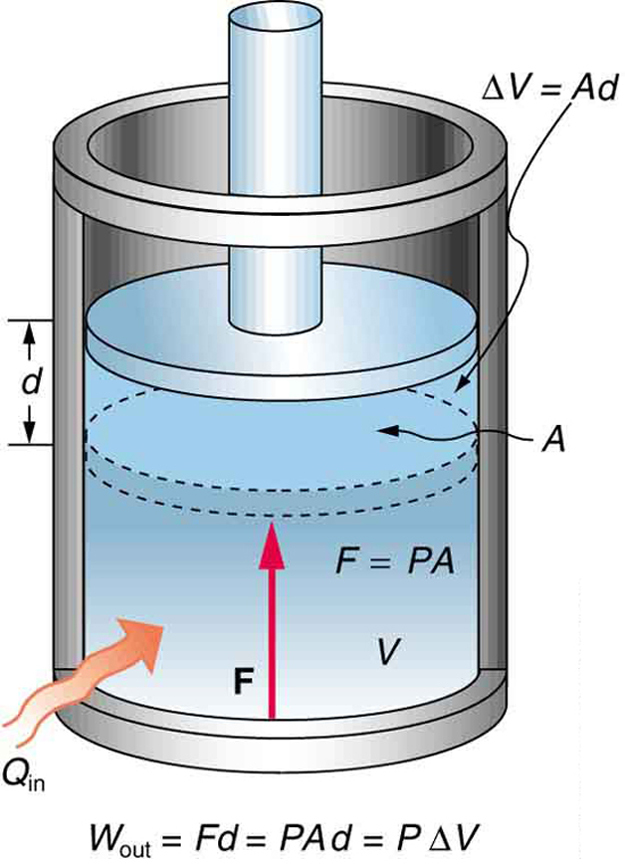
Work in a gas
Power
Power describes rate at which work is done. In the example above, if the box is pushed along faster, then more work is done per unit time. It is measured in Watt, where 1W represents the expenditure of 1 Joule per second.

Questions
Which of the following constitute work done ?
- Lifting 1 kg weight above your head
- Holding a 1kg weight above your head
- Blowing up a balloon
- Two snooker balls at the moment of collision
- A ball bearing rolling across a glass surface
Which of the processes associated with respiration store recoverable energy ?
- Hysteresis
- Recoil of alveolar surface tension
- Large airways resistance
- Recoil of lung tissue
- Small airways resistance
A plot of pressure against volume
- Allows compliance to be measured
- May show hysteresis
- Allows a direct measurement of airway resistance
- Is usually plotted on a semi-logarithmic paper
- Allows an estimate to be made of respiratory work
2. FTFTF
3. TTFFT